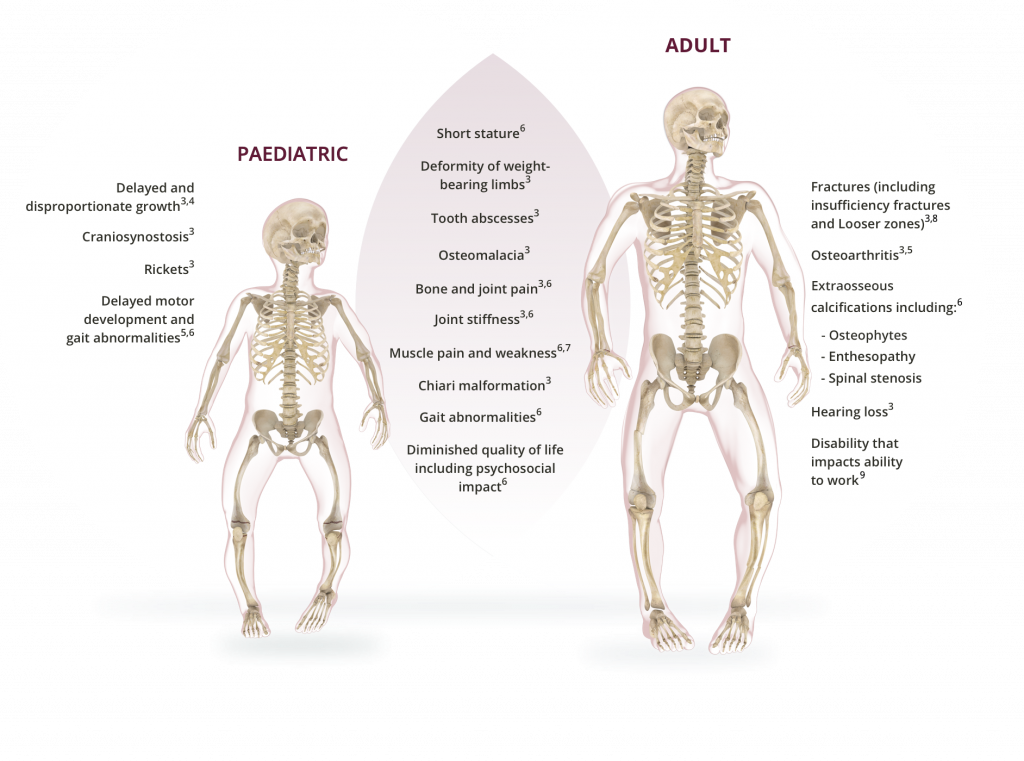
XLH is characterised by renal phosphate wasting, which is caused by excess fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) production1,2
1. Martin A, Quarles LD. Evidence for FGF23 involvement in a bone-kidney axis regulating bone mineralization and systemic phosphate and vitamin D homeostasis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;728:65-83. 2. Carpenter TO, Imel EA, Holm IA, Jan de Beur SM, Insogna KL. A clinician’s guide to X-linked hypophosphatemia. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(7):1381-1388. 3. Linglart A, Biosse-Duplan M, Briot K, et al. Therapeutic management of hypophosphatemic rickets from infancy to adulthood. Endocr Connect. 2014;3(1):R13-R30. 4. Zivičnjak M, Schnabel D, Billing H, et al. Age-related stature and linear body segments in children with X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets. Pediatr Nephrol. 2011;26(2):223-231. 5. Che H, Roux C, Etcheto A, et al. Impaired quality of life in adults with X-linked hypophosphatemia and skeletal symptoms. Eur J Endocrinol. 2016;174(3):325-333. 6. Skrinar A, Dvorak-Ewell M, Evins A, et al. The lifelong impact of X-linked hypophosphataemia: results from a burden of disease survey. J Endocr Soc. 2019;3(7):1321-1334. 7. Veilleux LN, Cheung M, Ben Amor M, Rauch F. Abnormalities in muscle density and muscle function in hypophosphatemic rickets. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2012;97(8):E1492-E1498. 8. Looser zones. Radiopaedia Web site. https://radiopaedia.org/articles/looser-zones-1. Accessed October 9, 2017. 9. Theodore-Oklota C, Bonner N, Spencer H et al. Qualitative research to explore the patient experience of X-linked hypophosphataemia and evaluate the suitability of the BPI-SF and WOMAC® as clinical trial end points. Value Health. 2018;21(8):973-983.
Patients and other health care providers may also know it as:
- X-linked hypophosphataemic rickets
- Genetic rickets
- X-linked vitamin D-resistant rickets
- Hypophosphataemic rickets
- Vitamin D-resistant rickets
- Hypophosphataemic vitamin D-resistant rickets
- Familial hypophosphataemic rickets
- X-linked rickets
- Hereditary hypophosphataemic rickets
- Familial hypophosphataemia
Role of FGF23
FGF23 is a protein hormone that regulates serum phosphate levels by suppressing both phosphate reabsorption in the kidney intestinal absorption of dietary phosphate. 6,7
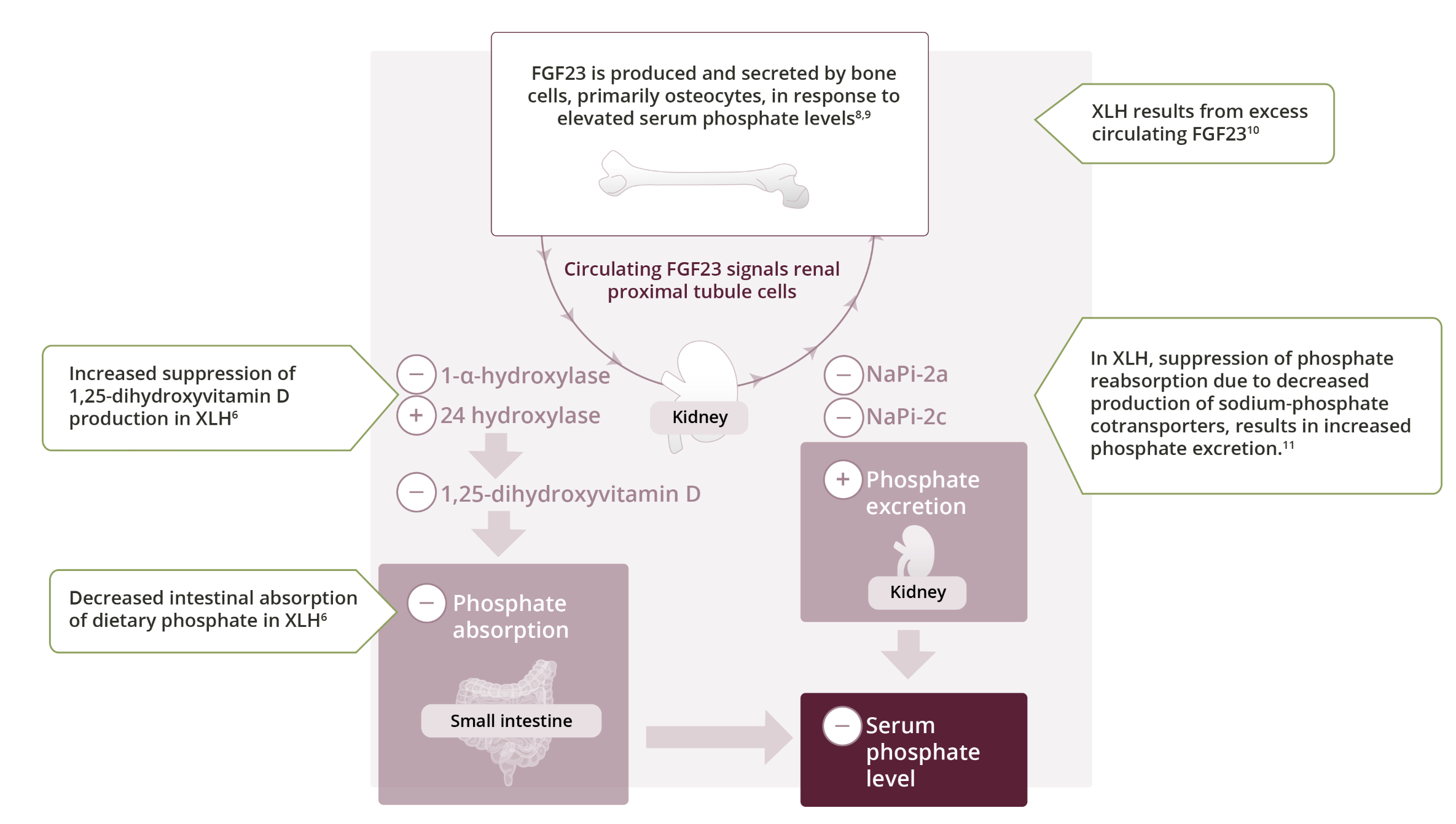
In patients with XLH, excess FGF23 leads to chronic hypophosphataemia caused by renal phosphate wasting and decreased intestinal absorption of phosphate 1,12,13
Low serum phosphate concentrations and reduced tubular reabsorption of phosphate corrected for glomerular filtration rate (GFR) are the characteristic laboratory findings in XLH patients 1
1. Ruppe, MD. X-linked hypophosphatemia. In: Pagon RA, Adam MP, Ardinger HH, et al, eds. Gene Reviews. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK83985/. Accessed October 20, 2017. 2. Hereditary Hypophosphataemic rickets. NIH Genetics Home Reference Web site. https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/hereditary-Hypophosphataemic-rickets. Accessed October 11, 2017. 3. Jackson WPU, Dowdle E, Linder GC. Vitamin-D-resistant osteomalacia. Brit Med J. 1958:1269-1274. 4. Rickets and osteomalacia. NHS Choices Web site. https://www.nhs.uk/Conditions/Rickets/Pages/Treatment. Accessed October 11, 2017. 5. Familial Hypophosphatemia. National Organization for Rare Disorders Web site. https://rarediseases.org/rare-diseases/familial-hypophosphatemia/. Accessed October 11, 2017. 6. Martin A, Quarles LD. Evidence for FGF23 involvement in a bone-kidney axis regulating bone mineralization and systemic phosphate and vitamin D homeostasis. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2012;728:65-83. 7. Schiavi SC. Fibroblast growth factor 23: the making of a hormone. Kidney Int. 2006;69(3):425-427. 8. Riminucci M, Collins MT, Fedarko NS, et al. FGF-23 in fibrous dysplasia of bone and its relationship to renal phosphate wasting. J Clin Invest. 2003;112(5):683-692. 9. Ferrari SL, Bonjour J-P, Rizzoli R. Fibroblast growth factor-23 relationship to dietary phosphate and renal phosphate handling in healthy young men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2005;90(3):1519-1524. 10. Che H, Roux C, Etcheto A, et al. Impaired quality of life in adults with X-linked hypophosphatemia and skeletal symptoms. Eur J Endocrinol. 2016;174(3):325-333. 11. Gattineni J, Bates C, Twombley K, et al. FGF23 decreases renal NaPi-2a and NaPi-2c expression and induces hypophosphatemia in vivo predominantly via FGF receptor 1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2009;297(2):F282-F291. 12. Carpenter TO, Imel EA, Holm IA, Jan de Beur SM, Insogna KL. A clinician’s guide to X-linked hypophosphatemia. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(7):1381-1388. 13. Penido MG, Alon US. Phosphate homeostasis and its role in bone health. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012;27(11):2039-2048.
With thanks to Kyowa Kirin International for prodiving graphics and citations
